Bronfenbrenner Development Theory

Urie Bronfenbrenner was an American nationalized Russian-born psychologist. His contributions were decisive for the theory of infant development. He proposed an ecological approach on the evolution of the individual by offering the systems of the surrounding environment a decisive role in the construction of the subject.
His was regarded as one of the most important emerging theories in developmental psychology. The theory of development of Bronfenbrenner argues that changes in an individual’s life are dictated mainly by the surrounding environment.
The influence of the context is multidirectional, that is, it has different effects depending on the culture. But it is also multicontextual and multicultural, that is, with incidence and interaction between different contexts and different cultures.
Over the course of his life, Urie Bronfenbrenner has received several awards for his work. He was also co-founder of an interesting program in the United States called Head Start, aimed at preschoolers with cognitive disabilities and adults.
The life of Urie Bronfenbrenner
Urie Bronfenbrenner was born in Moscow (Russia and the former Soviet Union) in 1917. Still very young, his family moved to the United States, where Bronfenbrenner lived until his death in 2005. His father was a doctor and became the director of New York. State Psychiatric Institute.
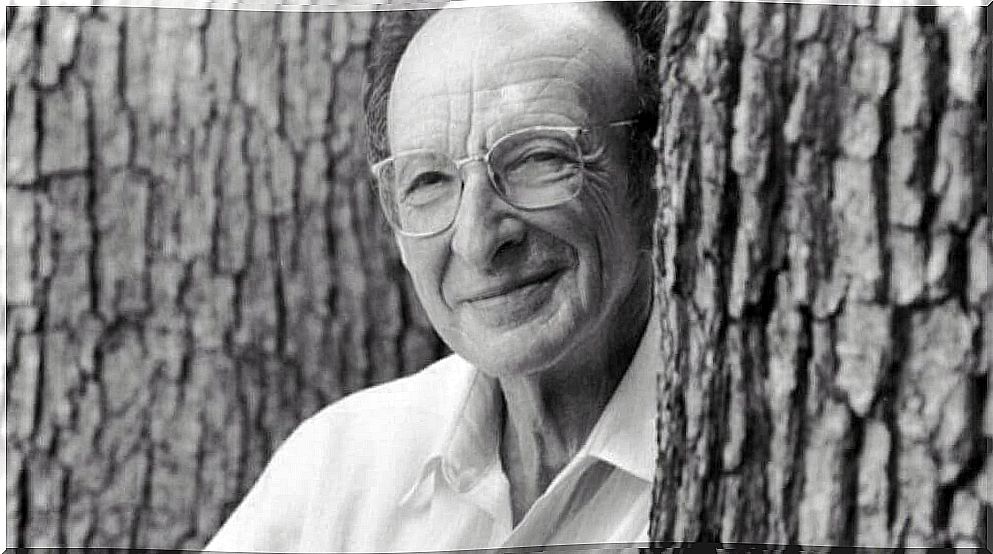

Urie Bronfenbrenner studied psychology and music at Cornell University and graduated in 1938. Later, he continued his studies in developmental psychology at Harvard and obtained his doctorate in this same discipline from the University of Michigan in 1942.
When World War II broke out, he worked as a psychologist in the ranks of the US military. This experience marked him deeply and offered him important foundations for the theory of development that he would propose at a later time.
After the war ended, Urie Bronfenbrenner devoted himself to teaching and research in various university centers. From his professorship and over the years he was concerned that his theories received practical translation into the lives of most people. To this end, he actively participated in the definition of some programs aimed at very young children and less fortunate sectors of society.
Bronfenbrenner’s theory of development
Urie Bronfenbrenner’s ideas are generically known as ecological systems theory. This development theory argues that different contexts have a decisive influence on the cognitive, moral and relational development of each individual.
It postulates the existence of four systems that envelop the subject and shape his conduct.

These systems are:
- Microsystem. It is the basic nucleus in which the individual moves. It includes family and school, or whatever takes its place.
- Mesosystem. Understands the constraints established by microsystems between them. For example, the relationship between family and school, or between teachers and family, etc.
- Macrosystem. Indicates the structural conditions. For example, culture, institutions, state policies, etc.
Urie Bronfenbrenner also speaks of ontosystem or biological and genetic characteristics of the single individual, of chronosystem or effect of historical time and globosystem or the incidence of great natural phenomena such as climate change, etc.
The contributions of Urie Bronfenbrenner
Based on a mutual influence between multiple contexts, Urie Bronfenbrenner argued that the different facts of the world affect and modify the individual. For example, he believed that the war in Syria was capable of altering an individual’s emotional state, although he did not directly suffer from the effects.
The main criticism leveled at Urie Bronfenbrenner’s theories comes from the cognitive-behavioral currents, according to which the scholar does not give sufficient importance to biological and cognitive factors in the development of the individual. They also question the absence of a succession of phases or stages in people’s evolutionary development.

Despite the criticisms, Urie Bronfenbrenner’s theory of development has become a landmark of the psychology of human development. This is because it showed and emphasized the influence of the environment on people. Although he was not the first scholar to do so, he nevertheless managed to give shape and coherence to these incidences, well beyond a general approach.